线程饥饿
2007年3月5日
在运行多次基准测试时,我发现 http_load 对某些连接出现了超时。在所有网络服务器以及 lighttpd 的不同后端中都观察到了这种情况。
在修补 http_load 以正确处理 超时 和 字节计数 错误后,我可以轻松地将超时与其他问题区分开来。在最近的一次变更集中,我添加了一个基础设施来跟踪单个连接在 lighttpd 中花费的时间,包括在 gthread-aio 后端的不同阶段花费的时间
- 调度线程读取(threaded-read())
- 在线程中启动读取(read())
- 等待其完成
- 将结果发送到主循环
- 将缓冲数据写入套接字
您可以通过设置定义 LOG_TIMING 来启用此计时。
network_gthread_aio.c.78: (trace) write-start: 1173101341.237616 read-queue-wait: 680 ms read-time: 0 ms write-time: 21 ms
network_gthread_aio.c.78: (trace) write-start: 1173101341.229014 read-queue-wait: 576 ms read-time: 0 ms write-time: 134 ms
network_gthread_aio.c.78: (trace) write-start: 1173101341.240815 read-queue-wait: 681 ms read-time: 6 ms write-time: 19 ms
我编写了一个脚本,从错误日志中提取这些计时数据,并使用 gnuplot 将其转换为图像
#!/bin/sh
## parse the errorlog for the lines from the timing_print
## - extract the numbers
## - sort it by start-time
## - make all timestamps relative to the first start-time
cat benchmark.error.log | \
grep "network_gthread_aio.c.78:" | \
awk '{ print $4,$6,$9,$12 }' | \
sort -n | \
perl -ne '@e=split / /;if (!$start) { $start = $e[0]; } $e[0] = $e[0] - $start; print join " ", @e; ' > $1.data
cat <<EOF
set autoscale
set terminal png
set xlabel "start-time of a request"
set ylabel "ms per request"
set yrange [0:30000]
set title "$1"
set output "$1.png"
plot \
"$1.data" using 1:2 title "read-queue-wait-time" with points ps 0.2, \
"$1.data" using 1:(\$2 + \$3) title "read-time" with points ps 0.2, \
"$1.data" using 1:(\$2 + \$3 + \$4) title "write-time" with dots
set title "$1 (read-queue-wait)"
set output "$1-read-queue-wait.png"
plot \
"$1.data" using 1:2 title "read-queue-wait-time" with points ps 0.8
set title "$1 (read)"
set output "$1-read.png"
plot \
"$1.data" using 1:3 title "read-time" with points ps 0.8 pt 2
set title "$1 (write)"
set output "$1-write.png"
plot \
"$1.data" using 1:4 title "write-wait-time" with points ps 0.8 pt 3
EOF
第一次基准测试耗时
./http_load -parallel 100 -fetches 500 ./http-load.10M.urls-10G
和
server.max-read-threads = 64
## compiled with 64k read-ahead
从磁盘读取数据所花费的时间增加
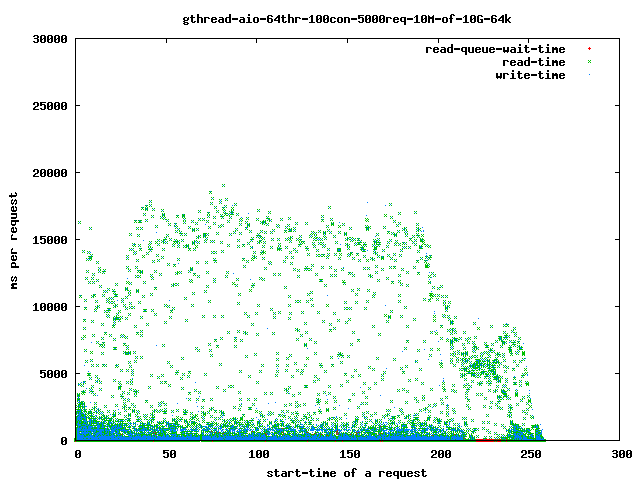
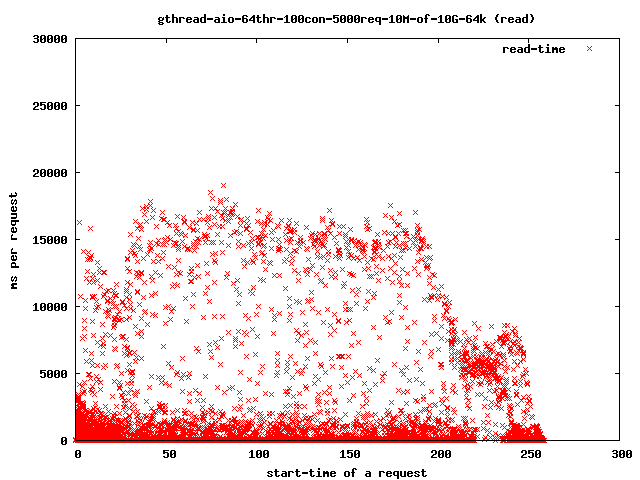
更多细节
如果将线程数减少到4,您会得到
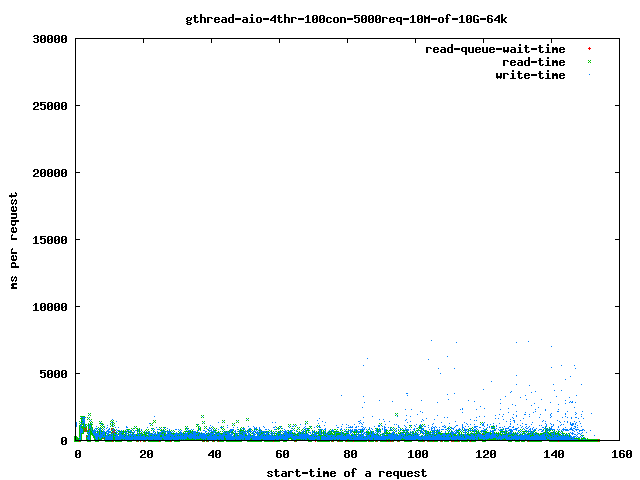
并且读取时间下降到
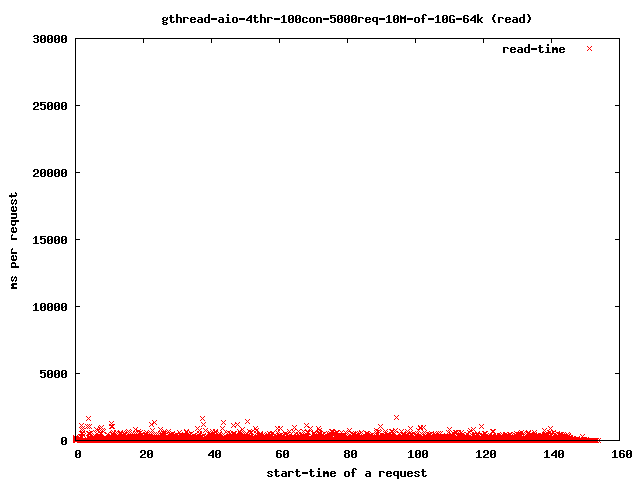
对我们的超时感兴趣的只是那些超出4秒范围的点,因为那些是我们的饥饿的读取()线程。如果它们完成耗时过长,客户端将关闭连接,用户将得到一个中断的传输。
减少线程数有助于限制问题的影响,正如我们在上面的图表中看到的
threads-runnable = threads-started - threads-blocked
随着被卡住的线程越来越多,可运行的线程越来越少,一个被卡住的线程再次获得CPU时间的概率会增加。在最坏的情况下,所有可用线程都在等待,并且至少有一个线程会完成。
更多图表
- 4个读取线程,10兆字节文件,64千字节预读
- 全部
- 读取队列等待
- 4个读取线程,10兆字节文件,1兆字节预读
- 全部
- 读取队列等待
- 读取
- 写入
- 64个读取线程,10兆字节文件,64千字节预读
- 全部
- 读取队列等待
- 读取
- 写入
- 64个读取线程,10兆字节文件,1兆字节预读
- 全部
- 读取
- 写入
经验法则
将最大线程数保持为磁盘数量的两倍。